Modern Standards-Based Education vs. Classical Education
Our colleague, Brandon Strong from Barry County Christian School, compiled this comparison. I find it helpful as I’m learning about the benefits of classical Christian education. As I review this comparison, I’m reminded of a highly informative series we watched - Mi-Education of America. Pete Hegseth paints of picture of what’s been happening with education; - https://nation.foxnews.com/the-miseducation-of-america/
Brandon Strong
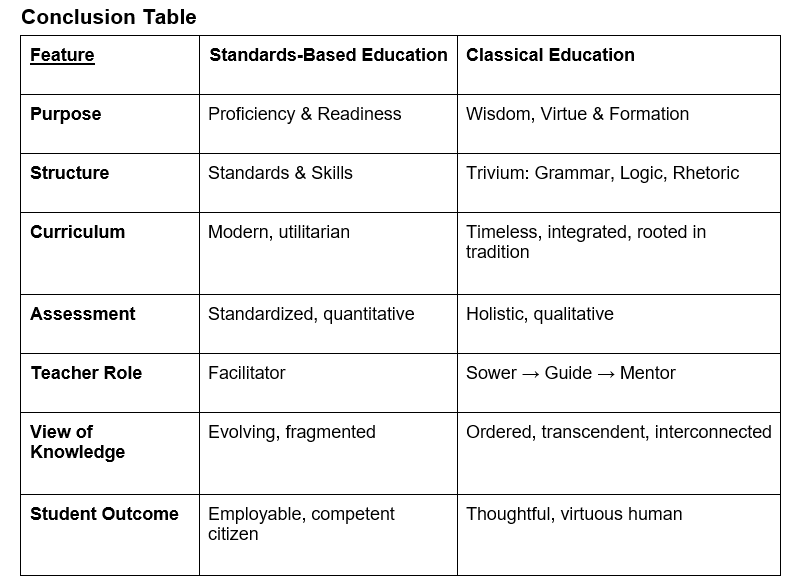
1. Philosophical Foundation
Standards-Based Education (SBE):
Rooted in progressivism and behaviorism.
Prioritizes measurable outcomes, career readiness, and skills application.
Seeks to produce competent individuals who meet state-defined benchmarks.
Classical Education:
Rooted in the Western tradition and often a Christian worldview.
Emphasizes the formation of the whole person—mind, body, and soul.
Seeks to cultivate wisdom, virtue, and a deep love for truth, goodness, and beauty.
2. Structure & Curriculum
Standards-Based:
Structured around grade-level standards in subject areas.
Curriculum is skills-based, focused on performance metrics and employability.
Emphasizes breadth over depth.
Classical:
Structured around the Trivium
Grammar (K–6): The Sower – Lays the foundation through memory work, language, math facts, Scripture, and stories.
Logic (7–9): The Guide – Teaches students how to think critically, ask questions, and reason well.
Rhetoric (10–12): The Mentor – Cultivates persuasive communication, character, and leadership.
Includes Latin, classical literature, formal logic, philosophy, and theology.
Prioritizes depth, integration, and enduring ideas.
3. View of the Student
Standards-Based:
Students are seen as individual learners moving through a defined set of standards.
Emphasis on data-driven instruction, closing achievement gaps, and differentiated outcomes.
Classical:
Students are seen as souls to be cultivated, not just minds to be measured.
Education is a formative process, shaping intellect, affections, and habits of virtue.
4. Assessment Methods
Standards-Based:
Relies heavily on standardized testing, rubrics, and frequent assessments.
Focus on quantifiable proficiency and accountability.
Classical:
Uses oral recitation, Socratic dialogue, essay writing, and formal presentations.
Focus on depth of understanding, clarity of thought, and ability to express truth eloquently.
5. Role of the Teacher
Standards-Based:
Teacher is a facilitator of learning.
Often follows a prescribed curriculum with limited flexibility.
Accountability is tied to student performance on standardized assessments.
Classical:
Teacher's role evolves with the Trivium:
Sower (Grammar): Plants seeds of truth and knowledge.
Guide (Logic): Leads students through structured reasoning.
Mentor (Rhetoric): Models wisdom and guides mature expression.
Emphasis on personal example, intellectual leadership, and moral formation.
6. Outcome Goals
Standards-Based:
Goal is to produce college- and career-ready citizens with 21st-century competencies.
Emphasizes efficiency, productivity, and adaptability.
Classical:
Goal is to form students who love learning, seek truth, and lead virtuous lives.
Education is a lifelong journey of becoming more human under God’s rule.